
SEO is more important than ever and continues to evolve. Now, the #1 result is no longer the most valuable, most visible position. Instead, Featured Snippets have given way to AI Overviews (AIOs) as the dominant results.
AI Overviews may seem to represent a threat to visibility but actually present a huge opportunity.
The good news? You don’t have to rank on page one to be cited in an AI Overview. But being cited in the most visible results like AI Overviews often depends on:
- Being seen as an authority on the topics you cover
- Structuring your content in a way that makes it genuinely useful to readers, easy to interpret, and parsable by machines
This step-by-step guide shows you how to optimize for AI Overviews. The secret to improving your chances of being cited lies in combining:
- Comprehensive information
- Clear writing
- Strategic formatting
- Essential SEO fundamentals
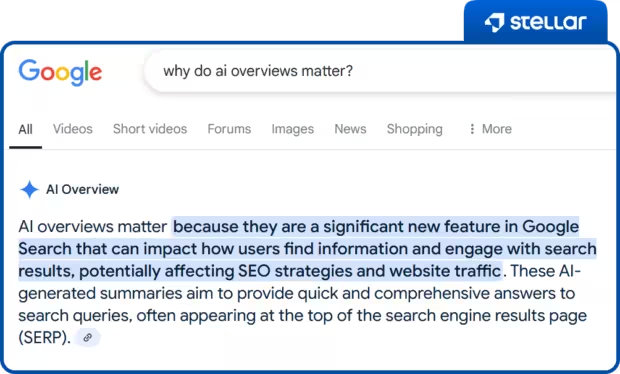
How do AI Overviews affect SEO?
AI Overviews matter because they’re becoming a prominent part of the search experience, especially for high-volume, informational queries. They currently appear in about 1 out of every 10 Google searches, and that number is expected to grow.
These summaries:
- Serve up the highest quality information
- Answer user questions directly on the results page
- Pull from multiple authoritative sources across the web
- Have effectively replaced Featured Snippets as the most valuable real estate in search
- Reduce work for users
AI Overviews are changing search by:
- Improving UX while reducing effort for users: Google’s mission is to make the world’s highest quality information as accessible as possible to as many as possible with a frictionless UX. That means reducing the number of actions searchers have to take (clicks) to find the information they seek as quickly and easily as possible. Featured Snippets pushed this trend. Now AIOs are the next phase in achieving this goal.
- Changing performance metrics: While traffic is still an important performance metric, AIOs are making impressions and authority just as important. Authority, as measured by citations like AIOs, Featured Snippets, and quality backlinks, indicates content quality and contributes to visibility. It’s the new key that helps position content to receive traffic. Authority, clarity, and structure matter more than ever. When your content is trusted and easy to extract, you’re more likely to earn a place in the Overview.
- Creating new opportunities for visibility: For marketers, that opens up a new path to visibility, even in competitive spaces. You’ve worked hard to optimize your content, and it ranks near the top of search results. But now, clicks are dropping. In fact, when Google includes an AI Overview, clicks fall by as much as 34%. Or maybe you’re not ranking on page one at all and looking for a new way to surface in search.
How to be cited in AI Overviews
Give your content the clarity, authority, and structure needed to earn a place in an AI Overview by following key best practices:
- Make content skimmable and digestible.
- Use clear and conversational language.
- Use relevant Related Questions in headings.
- Use tables when they improve clarity.
- Use lists and subheadings to increase extractability and readability.
- Link strategically using descriptive anchor text.
- Meet technical SEO and UX standards.
- Build topical authority over time.
Let’s take a closer look at these tips for strategically creating content.
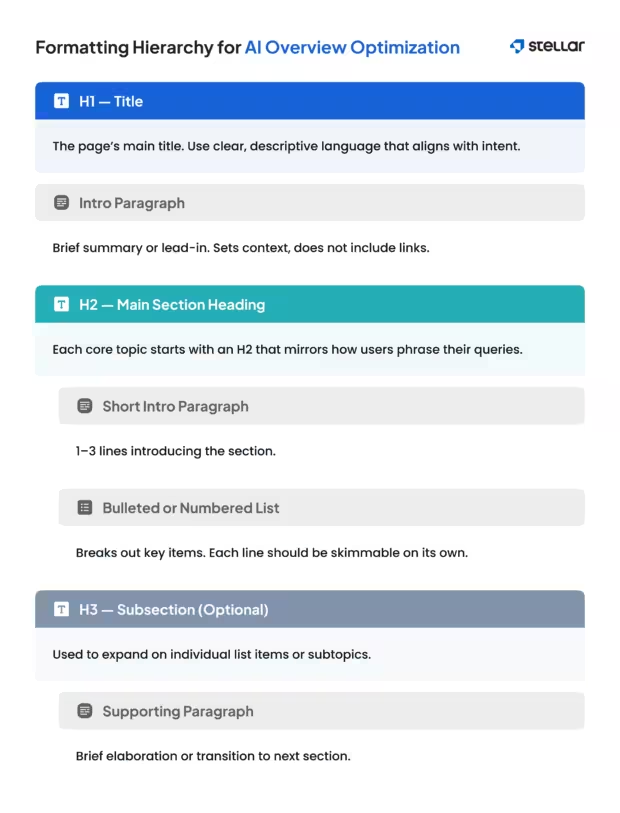
Step 1: Make content skimmable and digestible
Why it matters:
If your content isn’t clear and easy to consume, it won’t perform with readers or with AI. Dense paragraphs and unpredictable formatting create friction, reduce comprehension, and increase bounce rates.
The more quickly and confidently a reader can find what they need, the more likely they are to stay engaged. This is one big reason why listicles remain one of the most popular content formats.
How it helps you get cited:
AI Overviews are built to mimic how people gather and summarize answers. They scan content for structure, clarity, and relevance. Content that’s easy to scan, interpret, and extract is more likely to be cited even if it doesn’t rank on page one.
What to do
1. Use formatting that enhances readability:
- Keep paragraphs short (2–4 lines max).
- Use bulleted or numbered lists to break up dense information.
- Add subheadings to divide sections and guide the reader.
- Use white space intentionally to prevent visual overwhelm.
2. Present information in a predictable structure:
- Start sections with a clear heading or brief introductory line.
- Follow consistent formatting patterns (e.g., heading → short intro → list).
- Break out key information using bullets or numbers rather than comma-separated lists within a paragraph.
Pro tip
If you removed the paragraphs around your bullet points, would the bullets still make sense on their own? If not, revise them. Each list item should be independently helpful and skimmable.

Step 2: Use clear and conversational language
Why it matters:
When readers land on your content, they’re looking for quick clarity, not jargon, filler, or overly formal phrasing. If your writing feels dense, robotic, or vague, they’ll bounce. A clear, conversational tone makes content feel accessible, trustworthy, and easy to absorb.
How it helps you get cited:
AI Overviews are powered by large language models trained on human-like communication. They prioritize content that reads naturally and gets to the point. Writing that mimics how real people ask and answer questions increases your chances of being pulled into an Overview, especially for queries with high informational intent.
How to do it
- Use plain, natural language: Write like you’re explaining something to a curious peer.
- Avoid filler phrases and corporate jargon (e.g., “leveraging synergies,” “cross-functional alignment”).
- Stick to simple sentence structures when possible.
- Use contractions and first or second person where appropriate to keep the tone human.
- Be direct: Say what you mean in as few words as possible.
Pro tip
Before finalizing a paragraph, read it aloud. If it sounds like something you’d actually say in a conversation, you’re on the right track. If it sounds like something from a white paper or academic publication, cut it down or rephrase.
Step 3: Use relevant related questions as headings
Why it matters:
When people search, they don’t think in keywords — they think in questions. Using related questions as headings mirrors how your audience actually phrases their intent. It also tells readers (and search engines) that your content directly answers what people are asking, which builds trust and encourages continued engagement.
Search engines are so sophisticated now that they don’t just deal in keywords. Rather, they understand the underlying topics and concepts.
What’s more, the more specific the topic, the more likely it is to satisfy a person’s search. Think of Related Questions as the natural evolution of long-tail keywords.
How it helps you get cited:
AI Overviews often source content that clearly answers specific, high-intent queries. Related questions, pulled from tools like Google’s People Also Ask or the brief you’re working from, act as alignment signals.
When those exact phrases appear as headings, it increases your chances of being cited because it suggests your content is highly relevant and purpose-built to satisfy the query, which is a key signal if you want to rank in AI Overviews.
What to do
- Identify related questions using incognito Google searches, “People Also Ask,” or SEO tools like Semrush and Ahrefs.
- Match the exact phrasing where possible: Use the user’s language, not a reworded version.
- Use the question as the actual heading (e.g., H2 or H3) in your content.
- Answer the question directly beneath the heading with a concise, well-formatted response.
- If the question is complex, use lists or subheadings to break down the answer clearly.
Pro tip
Not all related questions appear in question form. Sometimes they’re statements (e.g., “best time to post on LinkedIn”). Don’t rephrase them. Use them as-is. That’s the phrasing your audience and the AIO system are using.
Step 4: Use lists and subheadings to increase extractability and readability
Why it matters:
Search engines and AI systems don’t just read your content; they try to extract and repurpose it. Lists and subheadings help them do that. When your content is clearly segmented and logically organized, it’s easier for Google to identify the most relevant parts and surface them in an AI Overview.
The reason this is important for search engines is that it’s helpful to human readers.
Target audiences tend to skim to understand if they’ve landed in the right place to find the information they seek. This approach helps make skimming easier and key information easier to find.
As a result, this kind of structure is more likely to:
- Send helpful signals
- Reduce work for users
- Improve engagement
- Reduce work for search engines
- Facilitate ranking
How it helps you get cited:
AI Overviews often pull from pages that clearly lay out information in a structured format. Lists and subheadings are high-value signals: They tell the system exactly what each section is about and make it easy to lift a discrete answer. That’s true whether your content is a how-to guide, product comparison, or best-practices roundup.
What to do
Use lists to make extractable chunks of information:
- Bullet unordered items like tips, tools, or pros and cons.
- Number sequences or step-by-step instructions.
- Use parallel structure (same syntax across list items) for clarity.
- When expanding on each item, use this format:
- Term: short, plain-language explanation
- Example: Content brief: a document that outlines key details about a specific piece of content
Use subheadings to clearly organize your content:
- When expanding on list items (like tools or types), give each one its own subheading.
- Example: A list of content tools can be followed by sections like “Grammarly,” “Trello,” and “Clearscope” as individual H3s.
- Match subheadings to list items exactly to help Google understand your structure and reuse it in AI Overviews.
- Use descriptive subheadings throughout your content, and avoid vague labels like “More info” or “Additional thoughts”.
Pro tip
If you’re listing items you plan to expand on later in the article, use the same phrasing in your subheadings. This creates a clear one-to-one connection that improves readability and reinforces structure for Google’s algorithms.
Step 5: Use tables when they improve clarity
Why it matters:
Some information is best understood at a glance. Tables allow you to present structured data, comparisons, or feature breakdowns in a way that’s visually efficient and easy to process. They work especially well when you need to show how similar items differ across categories, which can be hard to follow in paragraph form.
How it helps you get cited:
AI Overviews and other generative search products often favor content that’s clearly organized and easy to extract. Tables help search systems understand relationships between items by aligning data points in a predictable format. This makes it more likely that your content will be accurately interpreted and reused in an AI Overview or other search feature.
What to do
- Use tables to present:
- Feature or tool comparisons
- Pros and cons
- Pricing tiers or package options
- Specifications or attributes of related items
- Write clear and consistent column headers.
- Keep tables simple by limiting them to 2 to 5 columns.
- Use plain, scannable language inside each cell.
- Include a short introduction before the table and a summary or takeaway after it.
Pro tip
When comparing items like tools or service plans, ask yourself: Can a reader scan across a single row and clearly understand the differences? If not, consider simplifying the table or splitting it into smaller ones.
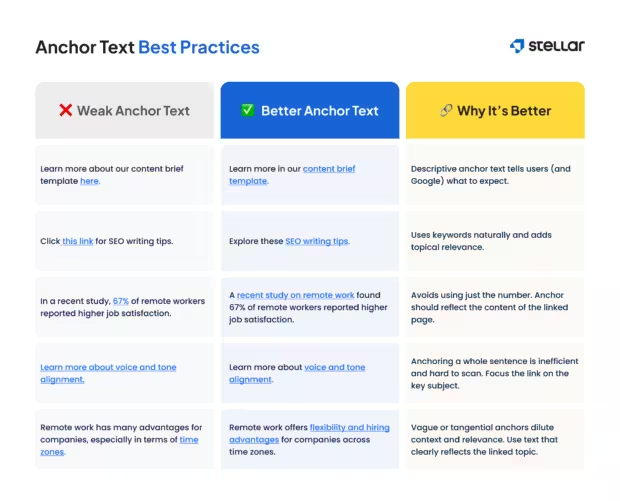
Step 6: Link strategically using descriptive anchor text
Why it matters:
Internal links help readers explore related content and stay engaged longer. They also guide search engines by showing how topics are connected across your site. But not all links are equally helpful. Poorly placed or vague links can confuse the reader or even hurt performance.
How it helps you get cited:
AI Overviews look for content that appears trustworthy, complete, and well-supported. Strategic internal linking helps reinforce topical authority and provides helpful context around a subject. Clear, descriptive anchor text also gives search engines better signals about what the linked page covers, which improves the odds of both pages being considered for citation.
What to do
- Use internal links to connect to:
- Deeper explanations of related topics
- Supporting content that adds value
- Key services, tools, or how-to resources
- Avoid linking in introductory sections where a reader might leave too early.
- Use anchor text that clearly describes the page being linked to.
- Example: “content brief template” instead of “click here”
- Place links where they feel natural and support the reader’s flow.
- Link sparingly — only when the connection genuinely adds context or clarity.
Pro tip
When reviewing your draft, scan your anchor text without the surrounding sentence. If the link still makes sense and tells the reader what to expect, you’re on the right track.
Step 7: Meet technical SEO and UX standards
Why it matters:
Even the best-written content can underperform if your site is difficult to navigate, slow to load, or poorly structured behind the scenes. Technical SEO and user experience (UX) are foundational. They ensure your content can be found, understood, and easily consumed by both people and search engines.
How it helps you get cited:
AI Overviews pull from sources that are accessible, crawlable, and trustworthy. Clean HTML, clear heading structures, and fast-loading pages all make it easier for Google to interpret your content. A positive UX keeps readers engaged, which may reinforce your page’s credibility and increase the likelihood of citation.
What to do
- Use semantic HTML to clearly define content sections.
- Follow a logical heading hierarchy (H1 for title, H2s for main sections, H3s within them).
- Add schema markup where appropriate to provide extra context.
- Optimize your page for mobile and fast load times.
- Remove intrusive popups or interstitials that disrupt reading.
- Ensure navigation is clean and consistent across the site.
Pro tip
Run your page through Google’s PageSpeed Insights and Mobile-Friendly Test before publishing. These tools can uncover issues that might block your content from being fully understood or surfaced in AI Overviews.
Step 8: Build topical authority over time
Why it matters:
Google rewards breadth as well as accuracy. Publishing a single great article on a subject isn’t always enough. When you consistently cover a topic from multiple angles, you demonstrate expertise and give both readers and search engines a reason to trust your content over others.
How it helps you get cited:
AI Overviews are more likely to cite sources that appear authoritative. By publishing a cluster of related content and linking it together, you send a strong signal that your site offers comprehensive coverage on the subject. That consistency builds trust, reinforces relevance, and increases your chances of being included in AIOs.
What to do
- Identify the topics that align your business products and services with your target audience’s interests, preferences, and pain points.
- Create content clusters by comprehensively covering a topic and its subtopics in dedicated articles.
- Use internal links to support sustained engagement, and avoid duplicate content by
connecting related pieces in a logical, reader-first way using relevant anchor text. - Avoid overlap and duplicate content by assigning a clear purpose to each page.
- Refresh content every 3–6 months to keep core pages up to date with new stats, examples, or best practices.
- Monitor performance and fill in gaps where supporting content is missing.
Pro tip
Think of your content like a map. If someone lands on any one piece, they should be able to explore nearby topics easily, and search engines should see a well-connected web of expertise.
Always keep E-E-A-T and search intent at the center
Formatting matters. So do structure, clarity, and technical performance. But none of it works unless your content is grounded in trust and aligned with what the reader actually wants.
AI Overviews are designed to deliver fast, reliable answers. That only happens when the content they pull from is credible and purpose-built to meet the searcher’s need.
That’s where E-E-A-T comes in.
Google looks for signals of experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness. If your content lacks depth, accuracy, or a clear point of view, it’s unlikely to be cited no matter how well it’s formatted.
If you’re not recognized as a trustworthy authority on a topic, you’re not likely to rank well (in AIOs or otherwise).
Equally important is understanding intent.
Before you write, ask what the reader is really trying to solve. Are they comparing options? Looking for a process? Trying to make a decision? Your structure and tone should follow from that goal.
When your content directly answers the right question — in the way the reader hopes to receive it — you earn both attention and authority.
Optimize with purpose
These are the AI Overview best practices we’ve found to be most effective.
Everything in this guide comes down to clarity and intention. When you write to genuinely help your reader and structure your content to make that help easy to access, you give yourself the best possible shot at earning visibility in AI Overviews.

