
Content marketing and digital marketing have plenty of overlap, but they’re not the same thing. They have distinct strategies, uses and best practices that we’ll cover, and each has experienced its own evolutionary path.
Content marketing leverages blogs, social posts, images and other types of online media to engage with a defined audience. It’s a subset of digital marketing.
Digital marketing employs multiple online and digital avenues to expand a company’s reach and drive conversions.
What is digital marketing?
Digital marketing is how companies promote their brand and products online. The practice began with the rise of the Internet and the release of the first ever search engine, Archie. It surged in popularity as the World Wide Web grew. Each new revolution in digital technology — such as the cookie, the smartphone and AI — brought similarly groundbreaking development in digital marketing.
Changes in digital marketing still come regularly. They’re often spearheaded by a shift in Google’s algorithms, which also help shape the digital marketing landscape. Today’s marketers understand that an effective digital marketing campaign doesn’t rely on one tried-and-true strategy — it’s a consistent effort to adapt to what audiences (and in turn, search engines) want..
Digital marketing channels and strategies
Digital marketing isn’t a cookie-cutter solution. Businesses have to rely on several channels working together, such as:
- Search engine optimization. SEO is the practice of organically improving a website’s visibility on popular search engines — though the primary target is usually Google. The concept can be further split into four buckets:
- On-page SEO. On-page SEO focuses on the content of a page. Is it helpful? Is it authoritative? Does it provide unique value to readers?
- Off-page SEO. Off-page SEO prioritizes the authority of a brand through high-quality backlinks (links from other pages to yours) and brand recognition. The content on your page doesn’t directly improve your off-page SEO, but it can have an impact if it encourages other trustworthy sites to link to yours.
- Technical SEO. Effective technical SEO provides an easy, convenient experience for your users through minimal load times, mobile optimization and an intuitive interface. It also emphasizes the use of proper tags, organization and naming conventions to help Google crawlers navigate and index a site.
- Local SEO. Local SEO makes sure businesses are visible to their target demographic. The goal is to appear in “near me” searches, and SEO experts achieve this through keyword targeting, localization of content and Google Business Profile optimization.
- Search engine marketing. Similar to SEO, the goal of SEM is to appear at the top of search engine results pages, but it relies on paid marketing instead of organic changes. Marketers research keywords with a potential for a high ROI and bid on sponsored placements at the top of SERPs.
- Pay-per-click advertising. PPC is another strategy that uses paid advertising for visibility on SERPs, but it has a different pricing model. Marketers pay each time their ad is clicked on. PPC and SEM cost more than SEO on average, but they can have an immediate effect, whereas SEO takes time to make an impact.
- Social media marketing. SMM builds a relationship with a business’s target audience using social media channels, whether it’s through text, video or any other form of media. Not every piece of SMM content pushes a product or service, though; posts are often made just to engage with customers and give a face to the brand.
- Email marketing. Email marketing provides businesses with a controlled way to engage with their audience. Targeted messages, such as product ads, newsletters and promos, are sent to specific audience members instead of being posted on a public forum.
- Display advertising. In display advertising, businesses create clickable ads that live on third-party resources. These can be videos, simple banners, animations or any other kind of display.
- Mobile marketing. Mobile marketing leverages mobile functions like QR codes, text messages, push notifications and in-app advertising to promote brands.
- Affiliate marketing. In affiliate marketing, a business pays a third-party entity, such as a social media influencer or a blogger with high site traffic, to promote their product or service. Generally, the affiliate earns commission for each lead generated through a specific link or a promo code.
- Online PR. PR is all about relationships. Experts cultivate and manage an online identity for a brand and use it to earn backlinks and mentions, build goodwill with the community and increase overall traffic.

What is content marketing?
Content marketing is a division of digital marketing that uses content to build and engage with an audience. Though it’s mostly online today, it didn’t start that way.
Content marketing has roots in early print publications when businesses (and Benjamin Franklin) would advertise their products and establish relationships with their communities. And as the limits of how far a company could reach were stretched, so were the limits of content marketing, whether it was through the use of magazines in the late 19th century or the marketing revolution of the internet.
However, marketers can’t just post anything — for content marketing to work, posts have to align with your audience’s expectations. They have to be helpful, easily digestible and visible in SERPs.
Is content marketing part of digital marketing?
Content marketing is one of many channels in digital marketing, but it’s an important one. An effective content marketing strategy doesn’t just drive traffic to your site — it builds your reputation in the community and positions you as an expert in the field. It encourages people to think of your business when they have a need in your industry.
Without quality content on your site, the rest of your digital marketing efforts won’t perform as well. Pages won’t rank organically without content to back them up, email and social campaigns won’t connect with the audience in the same way, and even paid ads won’t catch the right attention.
How does content marketing support digital marketing?
Content marketing supports digital marketing through:
- SEO. Well-written content can vastly improve the organic ranking of a page. It has the potential to help improve visibility, brand awareness, and engagement.
- Brand credibility and authority. Even if your site is visible, your audience needs to be able to trust you. Content that positions you as an expert provides that trust.
- Conversion rates. Content can be written to help readers make decisions between products and providers, leading them straight to your contact page.

Content marketing types and formats
Content isn’t just words on a page — it can be anything from a blog post to a podcast.
Consider these popular content types:
- Blog posts. Blog posts are probably the first thing that comes to mind when you hear “content.” This type of article typically targets a specific keyword and expands on the idea, sharing information with the reader.
- Landing pages. A landing page is where readers are redirected after they click on the link in an email or ad. The content on a landing page focuses on converting the reader to a customer.
- Videos and webinars. A video or a webinar is a sometimes-interactive piece of content designed to distill information to viewers in an easy-to-consume way. These could be prerecorded and posted on your site, or they may be live events where the host engages with viewers.
- Images. An image is a visual representation of info. These could be used to add to your blog posts, or they could be the main event.
- Infographics and visual content. Infographics explain concepts to viewers in a simplified, visual way. They’ve become more popular as people lean toward quick, bite-sized content.
- Podcasts. A podcast is a visual or auditory piece of online content that’s typically presented in episodes. Most of the content in a podcast is in the form of a conversation or a discussion with a real person.
- Case studies. Case studies are analyses of real-world situations with the goal of understanding the surrounding circumstances and the events that led to them.
- User-generated content. UGC is content that was created by users of a product or a service instead of by the provider. These can take the form of reviews, videos, images and more.
- Interactive content. Interactive content, like personality quizzes, engages with readers and provides a personalized experience.
- E-books. E-books are long-form pieces of content that can be downloaded. Usually, these establish authority and generate leads.
- Whitepapers. Similar to case studies, whitepapers are long-form pieces of content that analyze topics to inform readers. These documents typically aim to present the author as an expert.
What is an effective way for digital marketers to use content?
When it comes to content, you shouldn’t just throw words at the wall and see what sticks. Take these strategic steps to plan out and execute an effective marketing plan:
1. Understand your goals
Before you can do anything, you have to know why you’re doing it. Do you want to increase organic traffic to your site and heighten your conversion rates? Do you want to position yourself as a subject matter expert?
2. Identify your value propositions and your audience
Now, identify what makes you or your product different from your competitors. Ask yourself why readers should trust you instead of your competitor.
3. Know your audience
Examine the market to determine who you’re primary audience is. You can’t produce one piece of content for Gen Z artists and middle-aged business professionals — they won’t consume and appreciate it in the same way.
4. Research and select topics that align with your goals
Conduct research to find topics that are being searched, and make sure they’re relevant to your offerings. There may be a lot of search volume for a specific keyword like machine learning or AI, but that article won’t perform as well if it’s posted on a local coffee shop’s blog.
5. Conduct research to analyze intent
What a user means by their search is just as important as what they searched — if not more. Research ranking pages for your target keyword to determine what people are looking for. If they’re searching “phone cases” and the top 10 pages on the SERPs are all shops, a listicle may not be the way to go. If your keyword is “best phone cases,” though, the intent may align more with a listicle result.
6. Explore your competitors’ pages
Review your competitors’ pages — see what they’re doing well, and identify what they aren’t doing. If you can find a way to improve on what’s already out there, you may just take the number one spot.
7. Develop a strategy and content calendar
Outline a plan for what you need and how you’ll achieve it. Create an in-depth content calendar that specifies ownership, deadlines and any key information about each piece of content.
8. Create your content
Now, it’s time to create the content. If you aren’t able to create it yourself and haven’t hired an in-house creator, consider a third-party professional who can take this part off of your plate.
9. Identify core KPIs and consistently review
Think back to your goals.
- Are you trying to improve traffic? Then, measure how many people are entering your new pages.
- Trying to increase conversion rates? Compare the amount of people clicking on your content to the amount of people following the CTA.
If something isn’t working, don’t be afraid to adjust or redo.
10. Update and refresh often
Outdated content can harm a digital marketing campaign. This doesn’t mean you have to scrap older pieces — stats and links can be updated to fresh numbers, or an article can be repurposed into an infographic for a new take.
11. Align paid and organic efforts
Be aware of what paid and organic pages are performing well. If you have a page targeting a specific keyword that’s ranking well organically, using a PPC campaign to get more clicks may be a waste.
What are the differences between digital marketing and content marketing?
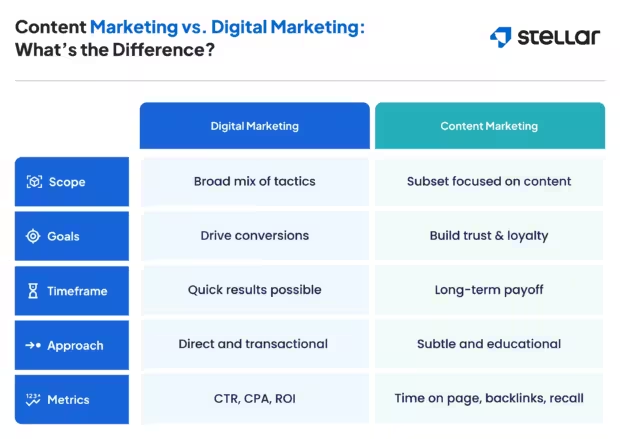
Content marketing is a vital subset of digital marketing, and a successful campaign treats them as distinct branches working in unison.
Remember these differences:
- Scope. Content marketing involves a lot of practices, but digital marketing encompasses all that and more.
- Goal. Digital marketing focuses on traffic and conversion, while the goal of content marketing is typically to build relationships and a recognizable name for your business.
- Timeframe. Some digital marketing efforts, like SEM, can have an immediate effect. Content marketing tends to take longer to see results.
- Approach. With digital marketing, many strategies like PPC campaigns and email marketing are direct. Content marketing subtly nudges readers toward businesses by building trust.
- Metrics. A successful digital marketing campaign might be marked by a 200% increase in website traffic year over year, while an effective content marketing campaign might be measured by your business’s position in the industry.
